MySQL で Entity Framework コードファーストのマイグレーションを利用してみました。
利用した際のライブラリのバージョンは次のとおりです。
- Entity Framework: 6.1.1
- MySQL.ConnectorNET.Entity: 6.8.3.2
結論から書くと、設定をちゃんと書けば、使えるレベルになってきてるな、というところです。以下、ASP.NET MVC で簡単な本の情報を扱うアプリケーションの作成を例に書いていきます。
まずは、プロジェクトの作成から。プロジェクト名は MysqlCodeFirstWithNoAuth02 として、「認証なし」なプロジェクトとします。
最初に NuGet から Entity Framework と MySQL.ConnectorNET.Entity を導入します(MySQL.ConnectorNET.Entity は mysql で検索すると出てきます)。
次に、アプリケーションで利用する MySQL のユーザーの作成とアプリケーション用の DB への権限付与をしておきます(DB 名: efcfSample02, DB ユーザー名: efcf01, DB ユーザーのパスワード: ******** とします)。
MySQL Command Line Client の例: grant all on efcfSample02.* to 'efcf01'@'localhost' identified by '********';
次に、プロジェクトのルートにある Web.config です。
...
<configuration>
<configSections>
<!-- For more information on Entity Framework configuration, visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=237468 -->
<section name="entityFramework" type="System.Data.Entity.Internal.ConfigFile.EntityFrameworkSection, EntityFramework, Version=6.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=自動生成された値" requirePermission="false" />
</configSections>
<connectionStrings>
<add name="BooksDb" connectionString="server=localhost;database=efcfSample02;uid=efcf01;password=********;charset=utf8" providerName="MySql.Data.MySqlClient" />
</connectionStrings>
<appSettings>
...
</runtime>
<entityFramework>
<defaultConnectionFactory type="System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.SqlConnectionFactory, EntityFramework" />
<providers>
<provider invariantName="System.Data.SqlClient" type="System.Data.Entity.SqlServer.SqlProviderServices, EntityFramework.SqlServer" />
<provider invariantName="MySql.Data.MySqlClient" type="MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlProviderServices, MySql.Data.Entity.EF6" />
</providers>
</entityFramework>
<system.data>
<DbProviderFactories>
<remove invariant="MySql.Data.MySqlClient" />
<add name="MySQL Data Provider" invariant="MySql.Data.MySqlClient" description=".Net Framework Data Provider for MySQL" type="MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlClientFactory, MySql.Data, Version=6.8.3.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=自動生成された値" />
</DbProviderFactories>
</system.data>
</configuration>次のことを行っています。
- connectionStrings の設定
- entityFramework の providers への MySql.Data.MySqlClient の追加(MySQL の Chapter 10 EF 6 Support を参照)
- system.data の DbProviderFactories の remove にある name="MySQL Data Provider" の削除(自動追加されるんですが、文法違反になっているという。。。バグですね。。。そのうち修正されるでしょう)
次にモデルを作成します。Models フォルダに Book クラスを追加します。
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace MysqlCodeFirstWithNoAuth02.Models
{
public class Book
{
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required]
[MaxLength(50, ErrorMessage = "タイトルの文字数は 50 文字までです。")]
public string Title { get; set; }
}
}次に DbContext です。プロジェクトに DAL フォルダを作成し、DAL フォルダに BooksContext クラスを追加します。
using System.Data.Common;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Data.Entity.Migrations.History;
using MySql.Data.Entity;
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient;
using MysqlCodeFirstWithNoAuth02.Models;
namespace MysqlCodeFirstWithNoAuth02.DAL
{
[DbConfigurationType(typeof(MysqlConfiguration))]
public class BooksContext : DbContext
{
public BooksContext() : base("BooksDb") { }
public DbSet<Book> Books { get; set; }
}
public class MysqlConfiguration : DbConfiguration
{
public MysqlConfiguration()
{
AddDependencyResolver(new MySqlDependencyResolver());
SetProviderFactory(MySqlProviderInvariantName.ProviderName, new MySqlClientFactory());
SetDefaultConnectionFactory(new MySqlConnectionFactory());
SetMigrationSqlGenerator(MySqlProviderInvariantName.ProviderName, () => new MySqlMigrationSqlGenerator());
SetProviderServices(MySqlProviderInvariantName.ProviderName, new MySqlProviderServices());
SetProviderFactoryResolver(new MySqlProviderFactoryResolver());
SetManifestTokenResolver(new MySqlManifestTokenResolver());
// __migrationHistory テーブルのデフォルト設定の変更
SetHistoryContext("MySql.Data.MySqlClient", (connection, defaultSchema) => new MyHistoryContext(connection, defaultSchema));
}
}
public class MyHistoryContext : HistoryContext
{
public MyHistoryContext(DbConnection dbConnection, string defaultSchema)
: base(dbConnection, defaultSchema)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
// 複合キー(MigrationId, ContextKey)の長さがデフォルトでは大きすぎるので設定を変更する
// 基底クラスの OnModelCreating(modelBuilder) でデフォルト設定を行っているので、base.OnModelCreating() の後に行うこと
modelBuilder.Entity<HistoryRow>().Property(h => h.MigrationId).HasMaxLength(100).IsRequired();
modelBuilder.Entity<HistoryRow>().Property(h => h.ContextKey).HasMaxLength(200).IsRequired();
}
}
}ここで行っているのが、MySQL 用の設定です。コメントにも書いていますが、マイグレーション用のデータを保存するテーブルの複合キーのデフォルトの長さが MySQL の制限にひっかかってしまうので、制限に引っかからないように最大長を設定しています(参考: Entity Framework with MySql and Migrations failing because “max key length is 767 bytes”)。
これでマイグレーションの準備ができました。
パッケージマネージャ コンソールで次のコマンドを入力します。
Enable-Migrations
Add-Migration InitialCreate
Update-Database
これで MySQL のデータベースが作成されて、テーブルも作成されています。
MySQL Command Line Client でテーブルの情報を確認したものが次のものです。
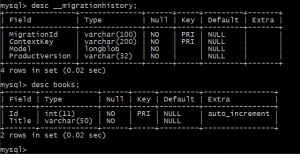
次にモデルの Book クラスに TitleYomigana を追加します(ついでに、このあとのアプリケーションの表示用に Display 属性も追加しています)。
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace MysqlCodeFirstWithNoAuth02.Models
{
public class Book
{
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required]
[Display(Name="書名")]
[MaxLength(50, ErrorMessage = "タイトルの文字数は 50 文字までです。")]
public string Title { get; set; }
[Required]
[Display(Name="よみがな")]
[MaxLength(100, ErrorMessage = "よみがなの文字数は 100 文字までです。")]
public string TitleYomigana { get; set; }
}
}パッケージマネージャ コンソールで次のコマンドを入力します。
Add-Migration AddBook_TitleYomigana
Update-Database
これで MySQL のテーブルに反映されています。
MySQL Command Line Client でテーブルの情報を確認したものが次のものです。
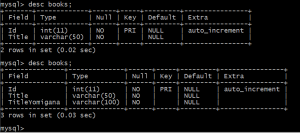
ということで、マイグレーションによる「DB 作成、テーブル作成、テーブルへの変更の反映」が問題なく行えています。なお、「Update-Database -TargetMigration: InitialCreate」コマンドを入力することで、データベースが InitialCreate の時点に戻ることも確認しました。
以降は、ついでということで、「一覧機能」「データ追加機能」まで実装してみます。
DAL フォルダに IBooksRepository インターフェイスを追加します。
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using MysqlCodeFirstWithNoAuth02.Models;
namespace MysqlCodeFirstWithNoAuth02.DAL
{
public interface IBooksRepository : IDisposable
{
IQueryable<Book> FindBooks();
Task<Book> GetBookAsync(int id);
Book AddBook(Book book);
void UpdateBook(Book book);
void DeleteBook(int id);
Task SaveAsync();
}
}DAL フォルダに BooksRepository クラスを追加します。
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using MysqlCodeFirstWithNoAuth02.Models;
namespace MysqlCodeFirstWithNoAuth02.DAL
{
public class BooksRepository : IBooksRepository
{
private BooksContext _context;
public BooksRepository()
{
_context = new BooksContext();
}
#region IBooksRepository メンバー
public IQueryable<Book> FindBooks()
{
IQueryable<Book> query = _context.Books.AsNoTracking().OrderBy(k => k.Id);
return query;
}
public Task<Book> GetBookAsync(int id)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public Book AddBook(Book book)
{
return _context.Books.Add(book);
}
public void UpdateBook(Book book)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public void DeleteBook(int id)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
public async Task SaveAsync()
{
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
#endregion
#region IDisposable メンバー
private bool _disposed = false;
/// <summary>
/// リソースの開放を行います。
/// </summary>
public void Dispose()
{
Dispose(true);
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
/// <summary>
/// リソースの開放を行います。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="disposing"></param>
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (_disposed) return;
_disposed = true;
if (disposing)
{
// マネージ リソースの解放処理
}
// アンマネージ リソースの解放処理
_context.Dispose();
}
#endregion
/// <summary>
/// デストラクタ
/// </summary>
~BooksRepository()
{
Dispose(false);
}
}
}DB への保存を 非同期メソッドで行うようにしています。
Controllers フォルダの HomeController を修正します。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using MysqlCodeFirstWithNoAuth02.DAL;
using MysqlCodeFirstWithNoAuth02.Models;
namespace MysqlCodeFirstWithNoAuth02.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
private readonly IBooksRepository _respository;
public HomeController() : this(new BooksRepository()) { }
public HomeController(BooksRepository repository)
{
_respository = repository;
}
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View(_respository.FindBooks());
}
public ActionResult Create()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
public async Task<ActionResult> Create(Book book)
{
try
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
_respository.AddBook(book);
await _respository.SaveAsync();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
return View(book);
}
catch
{
return View(book);
}
}
public ActionResult About()
{
ViewBag.Message = "Your application description page.";
return View();
}
public ActionResult Contact()
{
ViewBag.Message = "Your contact page.";
return View();
}
}
}Index アクションを右クリックし、「ビューの追加」を選択して、テンプレートを List、モデルクラスを Book にして、「追加」ボタンをクリックし、ビューを置き換えます。
Create アクションを右クリックし、「ビューの追加」を選択して、テンプレートを Create、モデルクラスを Book にして、「追加」ボタンをクリックし、ビューを作成します。
次の図は、これを動かして、データを追加してみた画面です。
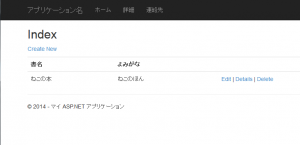
リポジトリで非同期メソッドの SaveChangesAsync を使いましたが、問題なく動いています 🙂
「MySQL で Entity Framework のマイグレーション」への1件のフィードバック